waterfall
Makie.waterfall Function
waterfall(x, y; kwargs...)Plots a waterfall chart to visualize individual positive and negative components that add up to a net result as a barplot with stacked bars next to each other.
Plot type
The plot type alias for the waterfall function is Waterfall.
Examples
using CairoMakie
y = [6, 4, 2, -8, 3, 5, 1, -2, -3, 7]
waterfall(y)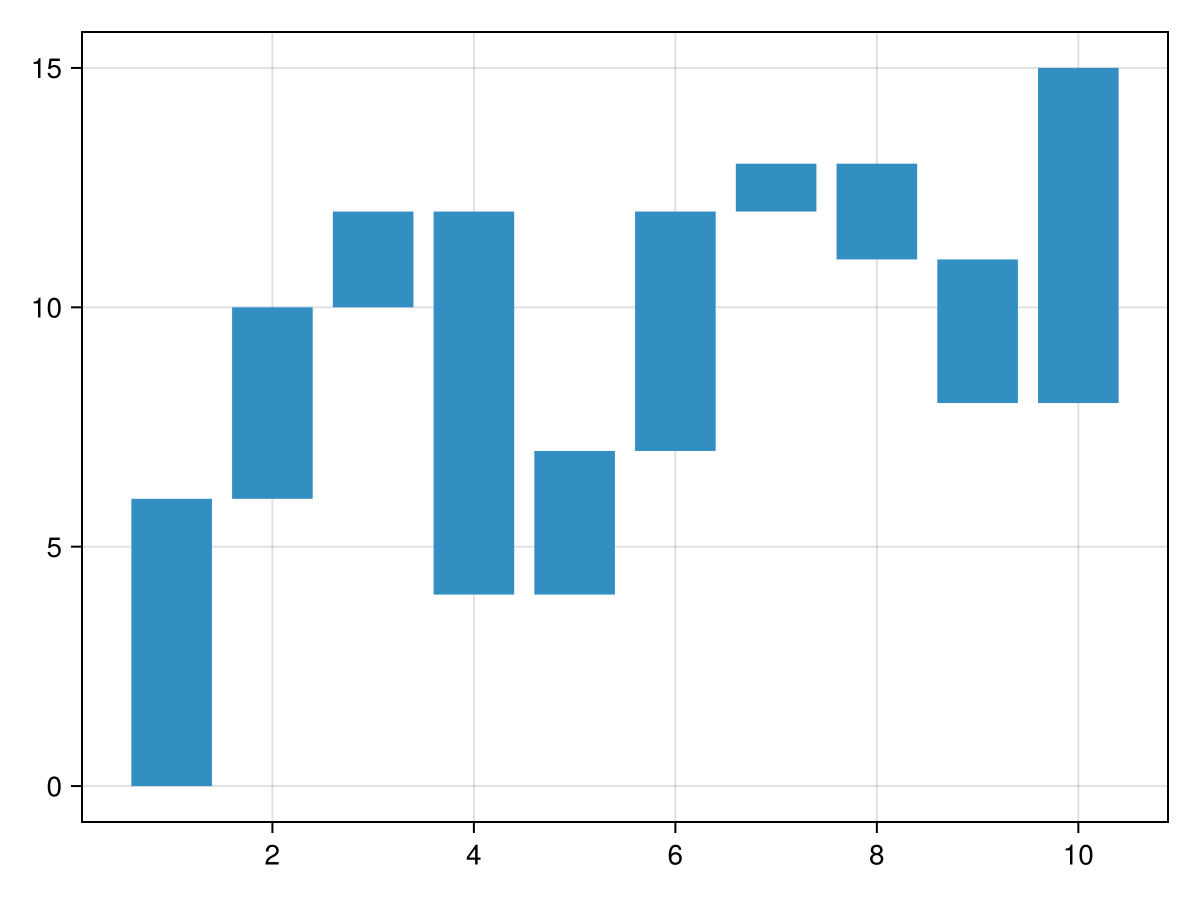
The direction of the bars might be easier to parse with some visual support.
using CairoMakie
y = [6, 4, 2, -8, 3, 5, 1, -2, -3, 7]
waterfall(y, show_direction=true)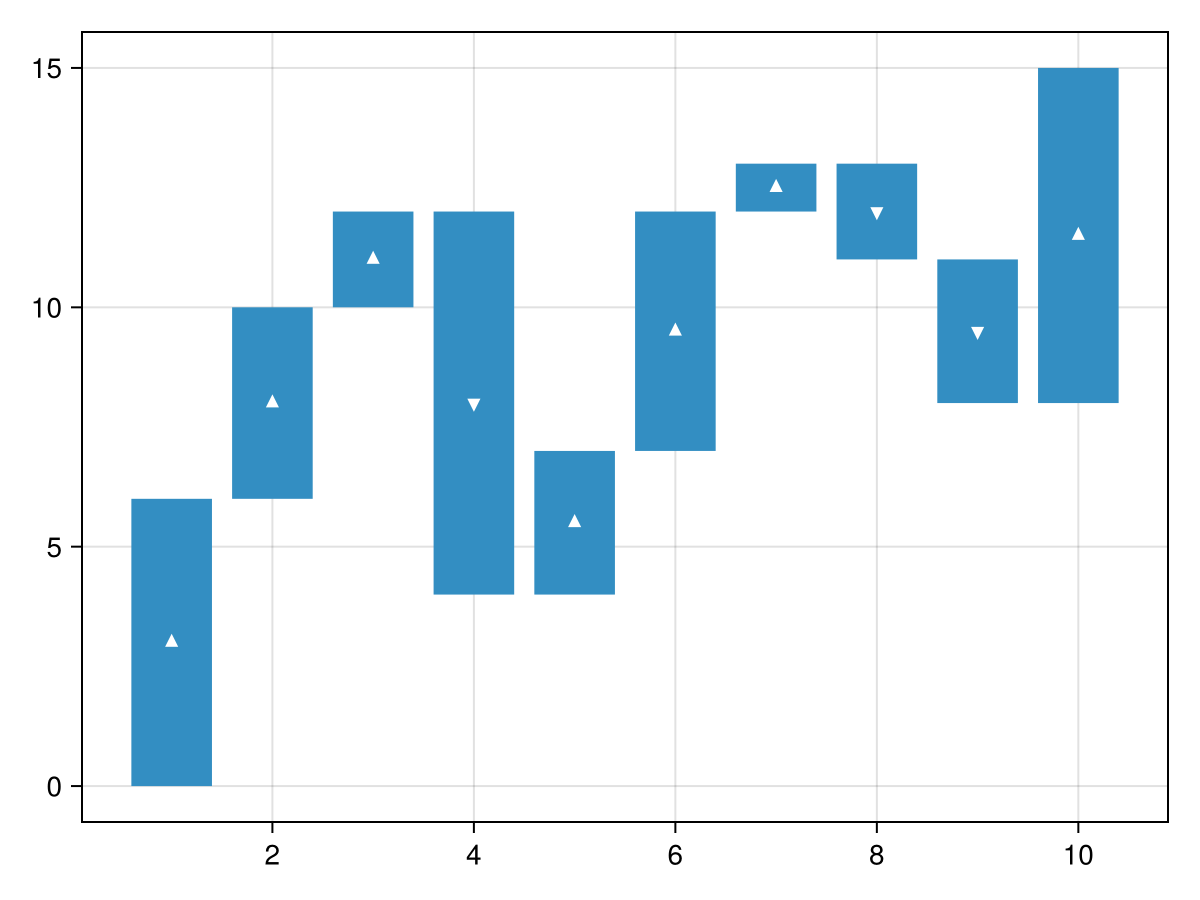
You can customize the markers that indicate the bar directions.
using CairoMakie
y = [6, 4, 2, -8, 3, 5, 1, -2, -3, 7]
waterfall(y, show_direction=true, marker_pos=:cross, marker_neg=:hline, direction_color=:gold)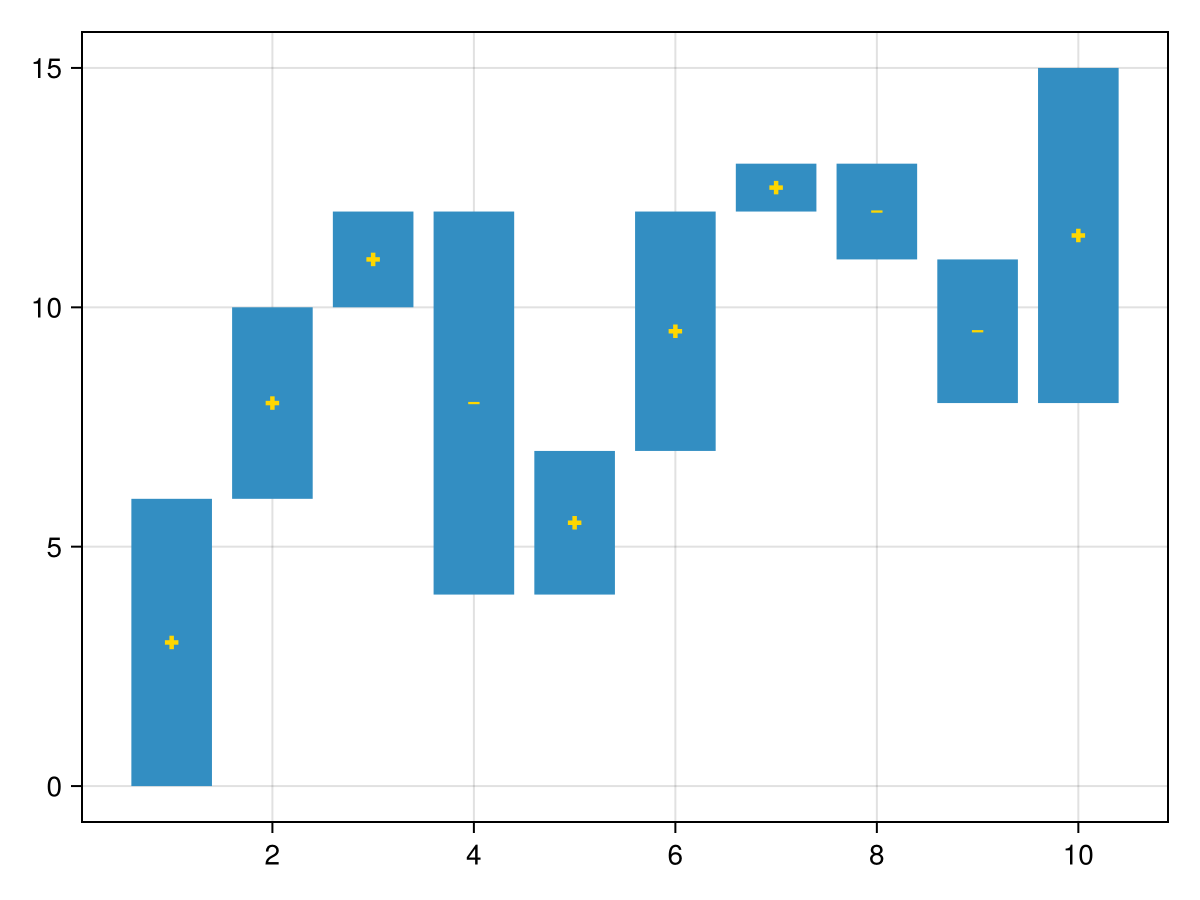
If the dodge attribute is provided, bars are stacked by dodge.
using CairoMakie
colors = Makie.wong_colors()
x = repeat(1:2, inner=5)
y = [6, 4, 2, -8, 3, 5, 1, -2, -3, 7]
group = repeat(1:5, outer=2)
waterfall(x, y, dodge=group, color=colors[group])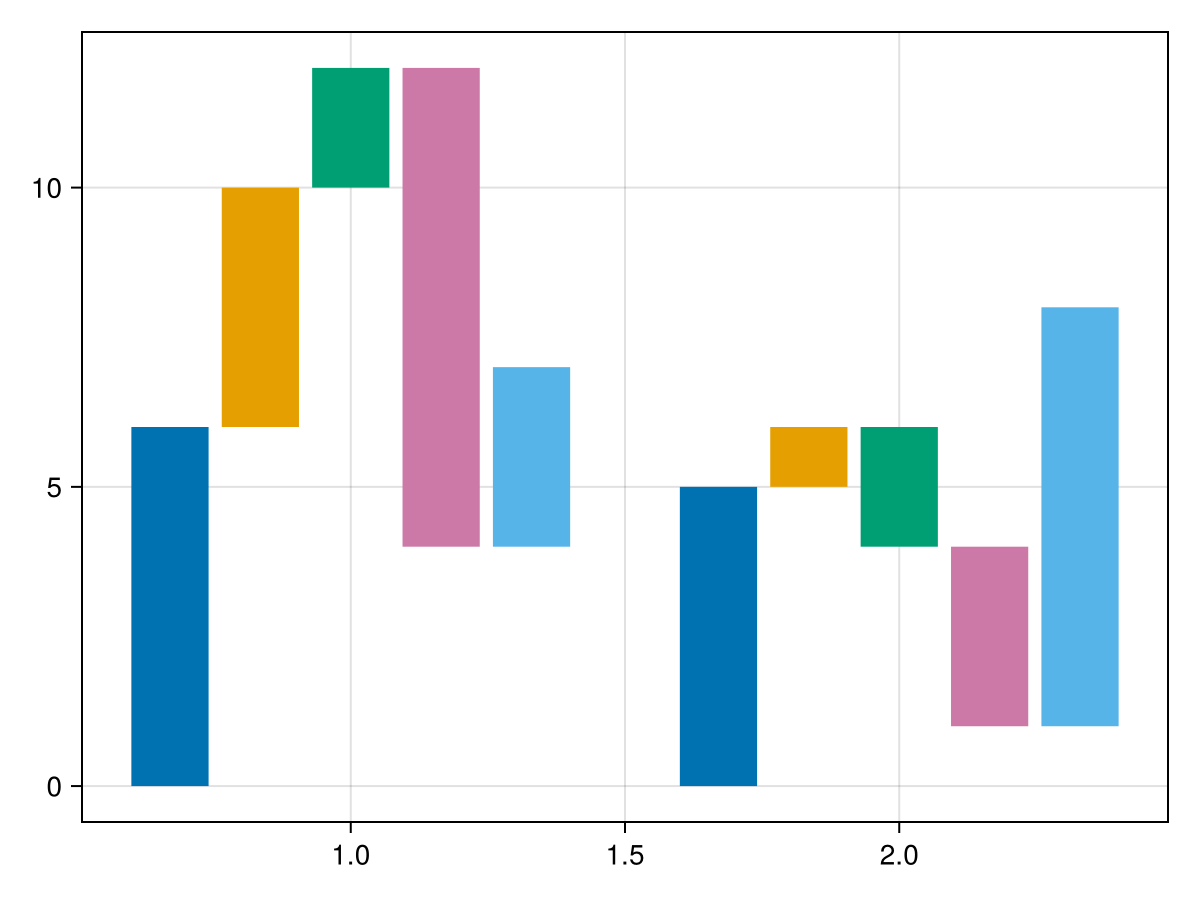
It can be easier to compare final results of different groups if they are shown in the background.
using CairoMakie
colors = Makie.wong_colors()
x = repeat(1:2, inner=5)
y = [6, 4, 2, -8, 3, 5, 1, -2, -3, 7]
group = repeat(1:5, outer=2)
waterfall(x, y, dodge=group, color=colors[group], show_direction=true, show_final=true)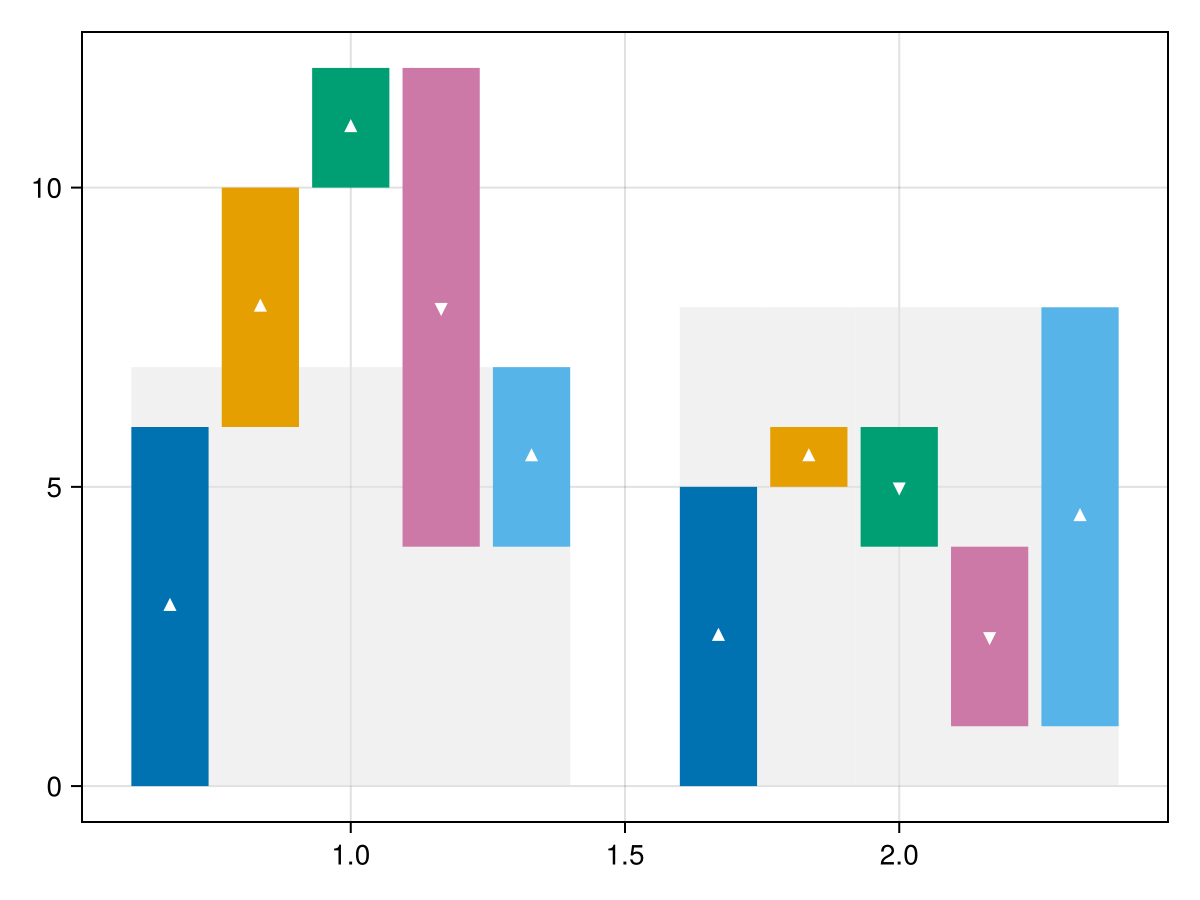
The color of the final bars in the background can be modified.
using CairoMakie
colors = Makie.wong_colors()
x = repeat(1:2, inner=5)
y = [6, 4, 2, -8, 3, 5, 1, -2, -3, 7]
group = repeat(1:5, outer=2)
waterfall(x, y, dodge=group, color=colors[group], show_final=true, final_color=(colors[6], 1//3))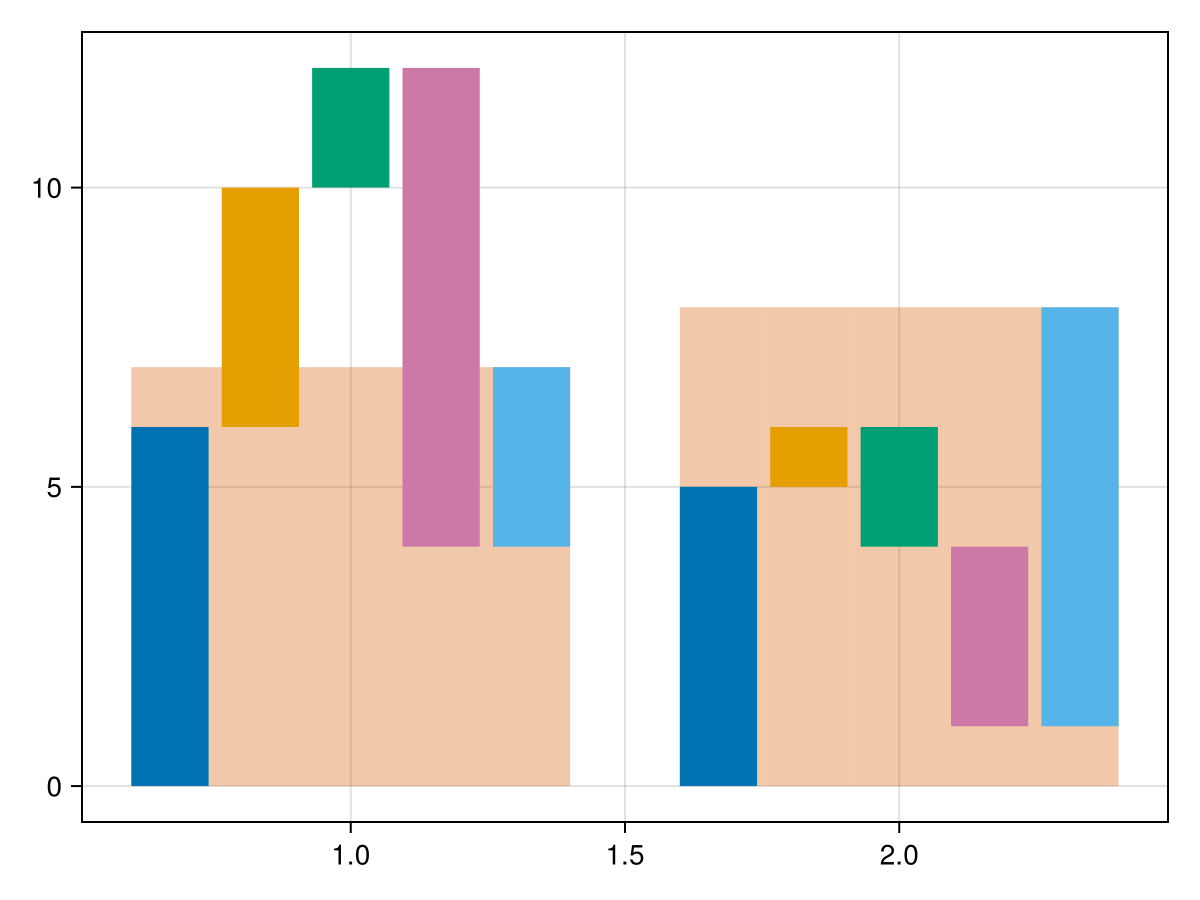
You can also specify to stack grouped waterfall plots by x.
using CairoMakie
colors = Makie.wong_colors()
x = repeat(1:5, outer=2)
y = [6, 4, 2, -8, 3, 5, 1, -2, -3, 7]
group = repeat(1:2, inner=5)
waterfall(x, y, dodge=group, color=colors[group], show_direction=true, stack=:x)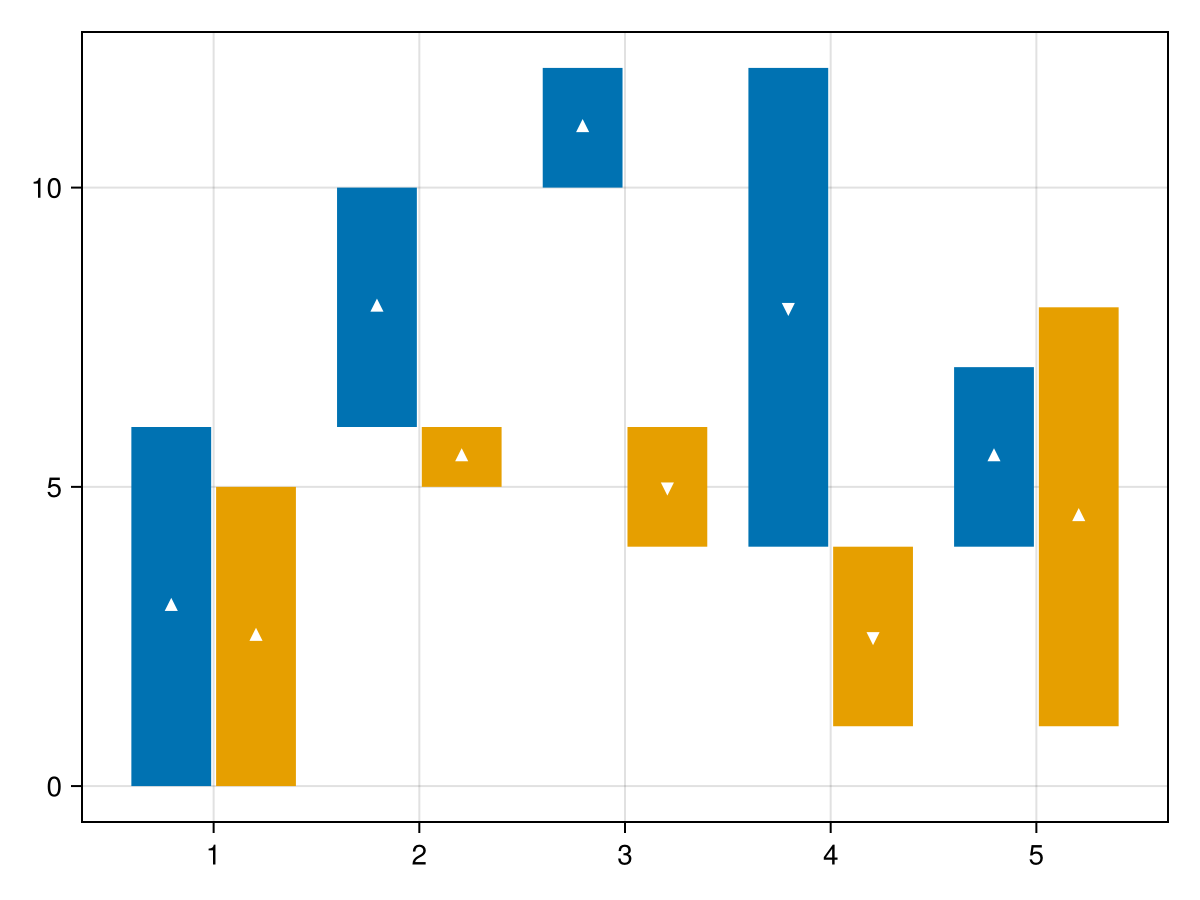
Attributes
alpha
Defaults to 1.0
The alpha value of the colormap or color attribute. Multiple alphas like in plot(alpha=0.2, color=(:red, 0.5), will get multiplied.
bar_labels
Defaults to nothing
Labels added at the end of each bar.
clip_planes
Defaults to @inherit clip_planes automatic
Clip planes offer a way to do clipping in 3D space. You can set a Vector of up to 8 Plane3f planes here, behind which plots will be clipped (i.e. become invisible). By default clip planes are inherited from the parent plot or scene. You can remove parent clip_planes by passing Plane3f[].
color
Defaults to @inherit patchcolor
Sets the color of bars.
color_over_background
Defaults to automatic
Sets the color of labels that are drawn outside of bars. Defaults to label_color
color_over_bar
Defaults to automatic
Sets the color of labels that are drawn inside of/over bars. Defaults to label_color
colormap
Defaults to @inherit colormap :viridis
Sets the colormap that is sampled for numeric colors. PlotUtils.cgrad(...), Makie.Reverse(any_colormap) can be used as well, or any symbol from ColorBrewer or PlotUtils. To see all available color gradients, you can call Makie.available_gradients().
colorrange
Defaults to automatic
The values representing the start and end points of colormap.
colorscale
Defaults to identity
The color transform function. Can be any function, but only works well together with Colorbar for identity, log, log2, log10, sqrt, logit, Makie.pseudolog10, Makie.Symlog10, Makie.AsinhScale, Makie.SinhScale, Makie.LogScale, Makie.LuptonAsinhScale, and Makie.PowerScale.
cycle
Defaults to [:color => :patchcolor]
Sets which attributes to cycle when creating multiple plots. The values to cycle through are defined by the parent Theme. Multiple cycled attributes can be set by passing a vector. Elements can
directly refer to a cycled attribute, e.g.
:colormap a cycled attribute to a palette attribute, e.g.
:linecolor => :colormap multiple cycled attributes to a palette attribute, e.g.
[:linecolor, :markercolor] => :color
depth_shift
Defaults to 0.0
Adjusts the depth value of a plot after all other transformations, i.e. in clip space, where -1 <= depth <= 1. This only applies to GLMakie and WGLMakie and can be used to adjust render order (like a tunable overdraw).
direction_color
Defaults to @inherit backgroundcolor
Color of the bar direction marker.
dodge
Defaults to automatic
Dodge can be used to separate bars drawn at the same position. For this each bar is given an integer value corresponding to its position relative to the given positions. E.g. with positions = [1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2] we have 3 bars at each position which can be separated by dodge = [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3].
dodge_gap
Defaults to 0.03
Sets the gap between dodged bars relative to the size of the dodged bars.
final_color
Defaults to plot_color(:grey90, 0.5)
Color of the final bar.
final_dodge_gap
Defaults to 0
Sets the dodge_gap of final bars.
final_gap
Defaults to automatic
Sets the gap of final bars. This defaults to 0 without dodge and gap with.
flip_labels_at
Defaults to Inf
Sets a height value beyond which labels are drawn inside the bar instead of outside.
fxaa
Defaults to true
Adjusts whether the plot is rendered with fxaa (fast approximate anti-aliasing, GLMakie only). Note that some plots implement a better native anti-aliasing solution (scatter, text, lines). For them fxaa = true generally lowers quality. Plots that show smoothly interpolated data (e.g. image, surface) may also degrade in quality as fxaa = true can cause blurring.
gap
Defaults to 0.2
The final width of the bars is calculated as w * (1 - gap) where w is the width of each bar as determined with the width attribute. When dodge is used the w corresponds to the width of undodged bars, making this control the gap between groups.
highclip
Defaults to automatic
The color for any value above the colorrange.
inspectable
Defaults to @inherit inspectable
Sets whether this plot should be seen by DataInspector. The default depends on the theme of the parent scene.
inspector_clear
Defaults to automatic
Sets a callback function (inspector, plot) -> ... for cleaning up custom indicators in DataInspector.
inspector_hover
Defaults to automatic
Sets a callback function (inspector, plot, index) -> ... which replaces the default show_data methods.
inspector_label
Defaults to automatic
Sets a callback function (plot, index, position) -> string which replaces the default label generated by DataInspector.
label_align
Defaults to automatic
Sets the text alignment of labels.
label_color
Defaults to @inherit textcolor
Sets the color of labels.
label_font
Defaults to @inherit font
The font of the bar labels.
label_formatter
Defaults to bar_label_formatter
Formatting function which is applied to bar labels before they are passed on text()
label_offset
Defaults to 5
The distance of the labels from the bar ends in screen units. Does not apply when label_position = :center.
label_position
Defaults to :end
The position of each bar's label relative to the bar. Possible values are :end or :center.
label_rotation
Defaults to 0π
Sets the text rotation of labels in radians.
label_size
Defaults to @inherit fontsize
The font size of the bar labels.
lowclip
Defaults to automatic
The color for any value below the colorrange.
marker_neg
Defaults to :dtriangle
Marker used for bars corresponding to negative y values.
marker_pos
Defaults to :utriangle
Marker used for bars corresponding to positive y values.
model
Defaults to automatic
Sets a model matrix for the plot. This overrides adjustments made with translate!, rotate! and scale!.
n_dodge
Defaults to automatic
Sets the maximum integer for dodge. This sets how many bars can be placed at a given position, controlling their width.
nan_color
Defaults to :transparent
The color for NaN values.
offset
Defaults to 0.0
Offsets all bars by the given real value. Can also be set per-bar.
overdraw
Defaults to false
Controls if the plot will draw over other plots. This specifically means ignoring depth checks in GL backends
show_direction
Defaults to false
When true, markers are drawn to indicate the direction of the bar.
show_final
Defaults to false
When true a bar with the total change is drawn. When dodge is used this bar is drawn per group.
space
Defaults to :data
Sets the transformation space for box encompassing the plot. See Makie.spaces() for possible inputs.
ssao
Defaults to false
Adjusts whether the plot is rendered with ssao (screen space ambient occlusion). Note that this only makes sense in 3D plots and is only applicable with fxaa = true.
stack
Defaults to automatic
Similar to dodge, this allows bars at the same positions to be stacked by identifying their stack position with integers. E.g. with positions = [1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2] each group of 3 bars can be stacked with stack = [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3].
strokecolor
Defaults to @inherit patchstrokecolor
Sets the outline color of bars.
strokewidth
Defaults to @inherit patchstrokewidth
Sets the outline linewidth of bars.
transformation
Defaults to :automatic
Controls the inheritance or directly sets the transformations of a plot. Transformations include the transform function and model matrix as generated by translate!(...), scale!(...) and rotate!(...). They can be set directly by passing a Transformation() object or inherited from the parent plot or scene. Inheritance options include:
:automatic: Inherit transformations if the parent and childspaceis compatible:inherit: Inherit transformations:inherit_model: Inherit only model transformations:inherit_transform_func: Inherit only the transform function:nothing: Inherit neither, fully disconnecting the child's transformations from the parent
Another option is to pass arguments to the transform!() function which then get applied to the plot. For example transformation = (:xz, 1.0) which rotates the xy plane to the xz plane and translates by 1.0. For this inheritance defaults to :automatic but can also be set through e.g. (:nothing, (:xz, 1.0)).
transparency
Defaults to false
Adjusts how the plot deals with transparency. In GLMakie transparency = true results in using Order Independent Transparency.
visible
Defaults to true
Controls whether the plot gets rendered or not.
width
Defaults to automatic
The gapless width of the bars. If automatic, the width w is calculated as minimum(diff(sort(unique(positions))). The actual width of the bars is calculated as w * (1 - gap).