Lighting
The Lighting capabilities of Makie differ between backends and plot types. They are implemented for mesh related plot types (mesh, meshscatter, surface), their derivatives (e.g. 3D arrows) and to some degree volume plots (and contour3d). With respect to Backends:
GLMakie implements the baseline lighting model and will act as our default for this page.
WGLMakie implements a simplified version of GLMakie's lighting.
CairoMakie implements limited lighting due to its limited 3D capabilities
RPRMakie implements parts of Makies lighting model but can also use more sophisticated methods from RadeonProRender.
Material Attributes
In 3D rendering a material describes how an object reacts to light. This can include the color of an object, how bright and sharp specular reflections are, how metallic it looks, how rough it is and more. In Makie however the model is still fairly simple and limited. Currently the following material attributes are available:
diffuse::Vec3f = Vec3f(1.0): controls how strong the diffuse reflections of an object are in the red, green and blue color channel. A diffuse reflection is one where incoming light is scattered in every direction. The strength of this reflection is based on the amount of light hitting the surface, which is proportional todot(light_direction, -normal). It generally makes up the main color of an object in light.specular::Vec3f = Vec3f(0.4): controls the strength of specular reflection in the red, green and blue color channels. A specular reflection is a direct reflection of light, i.e. one where the incoming angledot(light_direction, -normal)matches the outgoing angledot(camera_direction, -normal). It responsible for bright spots on objects. Note that this does not take the color of the object into account, as specular reflections typically match the light color.shininess::Float32 = 32f0: controls how sharp specular reflections are. Low shininess will allow a larger difference between incoming outgoing angle to take effect, creating a larger and smoother bright spot. High shininess will respectively reduce the size of the bright spot and increase its sharpness. This value must be positive.backlight::Real = 0controls how strongly light interacts with the backside of an object. Setting this to a value> 0can be helpful when visualizing a surface. (More precisely the light calculation is repeated with inverted normals and the result is mixed in withbacklightas a prefactor.)
Note
RPRMakie does not use these material attributes. Instead it relies on RadeonProRender's material system, which is passed through the material attribute. See the RPRMakie page for examples.
Lighting algorithm
Lights are controlled through the lights vector in a scene and by the shading attribute in a plot. Generally you will not need to set shading yourself, as it is derived based on the lights vector. The possible options for shading are:
shading = NoShadingdisables light calculations, resulting in the plain color of an object being shown.shading = FastShadingenables a simplified lighting model which only allows for oneAmbientLightand oneDirectionalLight.shading = MultiLightShadingis a GLMakie exclusive option which enables multiple light sources (as set in theScreenConfig, default up to 64) as well asPointLightandSpotLight.shading = Makie.automaticderive one of the above options based on the lights inscene.lights
Note
You can access the underlying scene of an Axis3 with ax.scene.
For reference all the lighting calculations (except ambient) in GLMakie, WGLMakie and to some extend CairoMakie end up using the Blinn-Phong reflection model which boils down to
function blinn_phong(
diffuse, specular, shininess, normal, object_color,
light_color, light_direction, camera_direction
)
diffuse_coefficient = max(dot(light_direction, -normal), 0.0)
H = normalize(light_direction + camera_direction)
specular_coefficient = max(dot(H, -normal), 0.0)^shininess
return light_color * (
diffuse * diffuse_coefficient * object_color +
specular * specular_coefficient
)
endThe different light sources control the light_direction and may further adjust the result of this function. For example, SpotLight adds a factor which reduces light intensity outside its area.
Types of Light
AmbientLight
using CairoMakie
fig = Figure(size = (600, 600))
ax11 = LScene(fig[1, 1], scenekw = (lights = [],))
ax12 = LScene(fig[1, 2], scenekw = (lights = [AmbientLight(RGBf(0, 0, 0))],))
ax21 = LScene(fig[2, 1], scenekw = (lights = [AmbientLight(RGBf(0.7, 0.7, 0.7))],))
ax22 = LScene(fig[2, 2], scenekw = (lights = [AmbientLight(RGBf(0.8, 0.3, 0))],))
for ax in (ax11, ax12, ax21, ax22)
mesh!(ax, Sphere(Point3f(0), 1f0), color = :white)
end
fig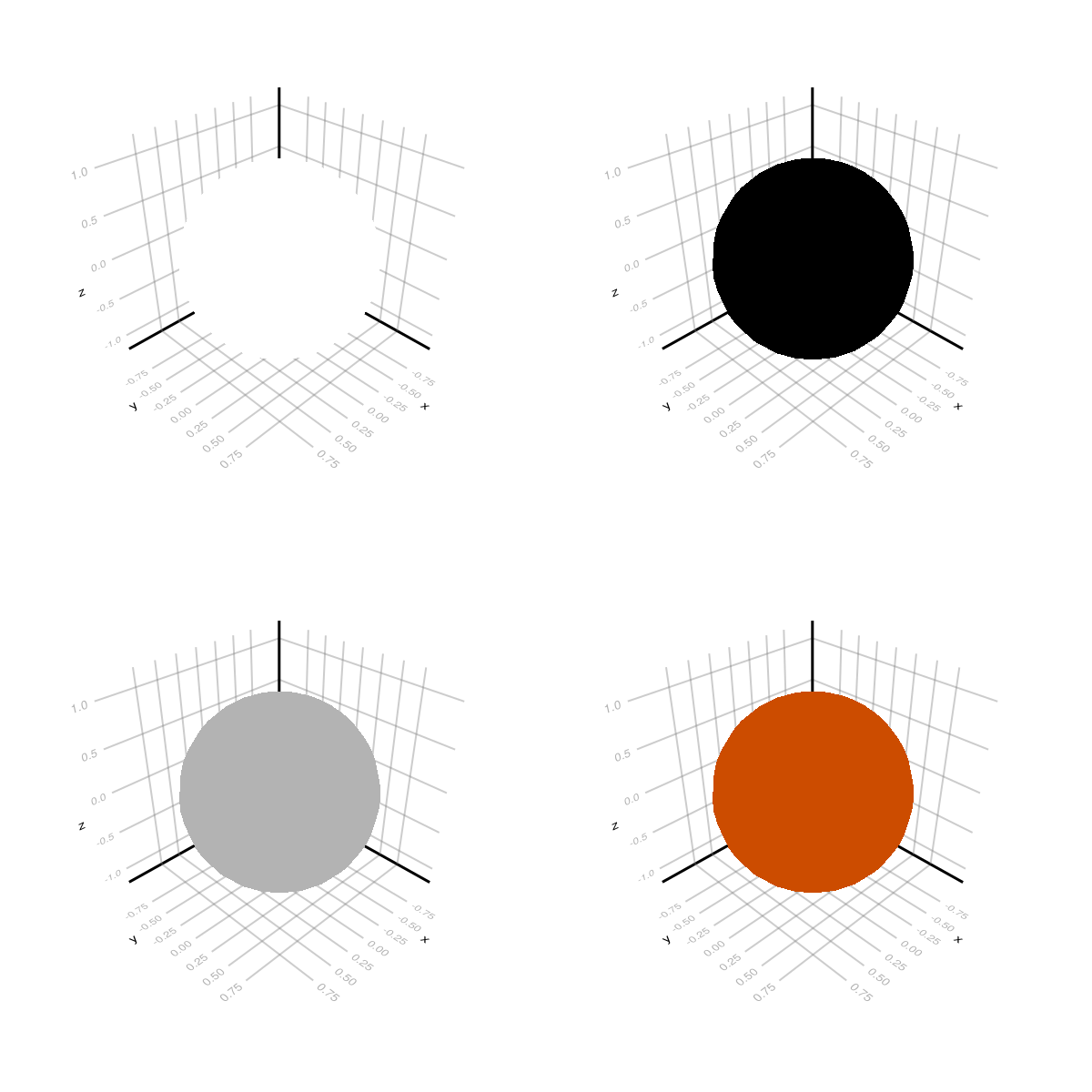
DirectionalLight
using GLMakie
fig = Figure(size = (600, 600))
ax11 = LScene(fig[1, 1], scenekw = (lights = [DirectionalLight(RGBf(0, 0, 0), Vec3f(-1, 0, 0))],))
ax12 = LScene(fig[1, 2], scenekw = (lights = [DirectionalLight(RGBf(1, 1, 1), Vec3f(-1, 0, 0))],))
lights = [
DirectionalLight(RGBf(0, 0, 0.7), Vec3f(-1, -1, 0)),
DirectionalLight(RGBf(0.7, 0.2, 0), Vec3f(-1, 1, -1)),
DirectionalLight(RGBf(0.7, 0.7, 0.7), Vec3f(1, -1, -1))
]
ax21 = LScene(fig[2, 1], scenekw = (lights = lights,))
ax22 = LScene(fig[2, 2], scenekw = (lights = [DirectionalLight(RGBf(4, 2, 1), Vec3f(0, 0, -1))],))
for ax in (ax11, ax12, ax21, ax22)
mesh!(ax, Sphere(Point3f(0), 1f0), color = :white)
end
fig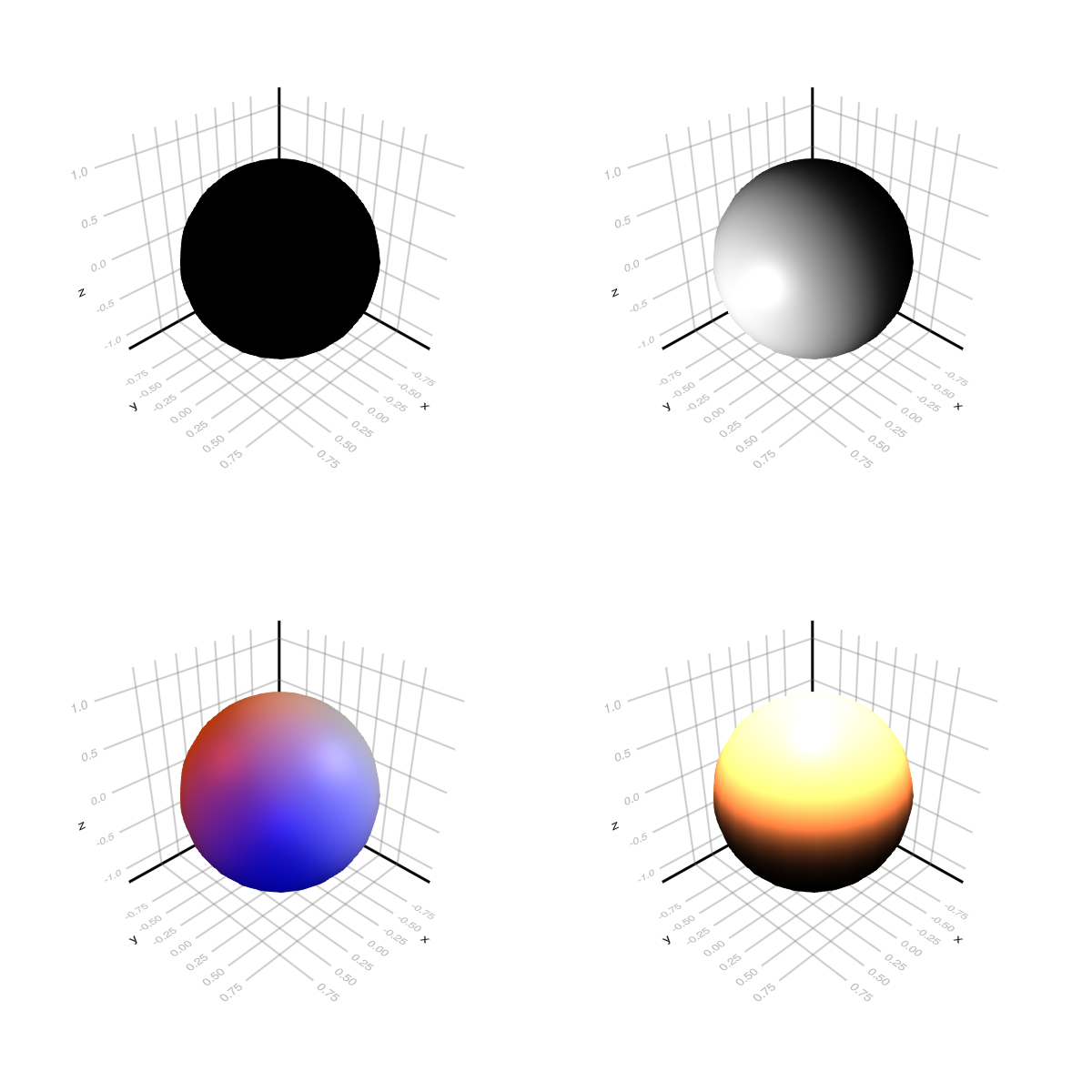
PointLight
using GLMakie
fig = Figure(size = (600, 600))
ax = LScene(fig[1, 1], scenekw = (lights = [PointLight(RGBf(1, 1, 1), Point3f(0, 0, 0))],))
ps = [Point3f(x, y, z) for x in (-1, 0, 1) for y in (-1, 0, 1) for z in (-1, 0, 1)]
meshscatter!(ax, ps, color = :white)
fig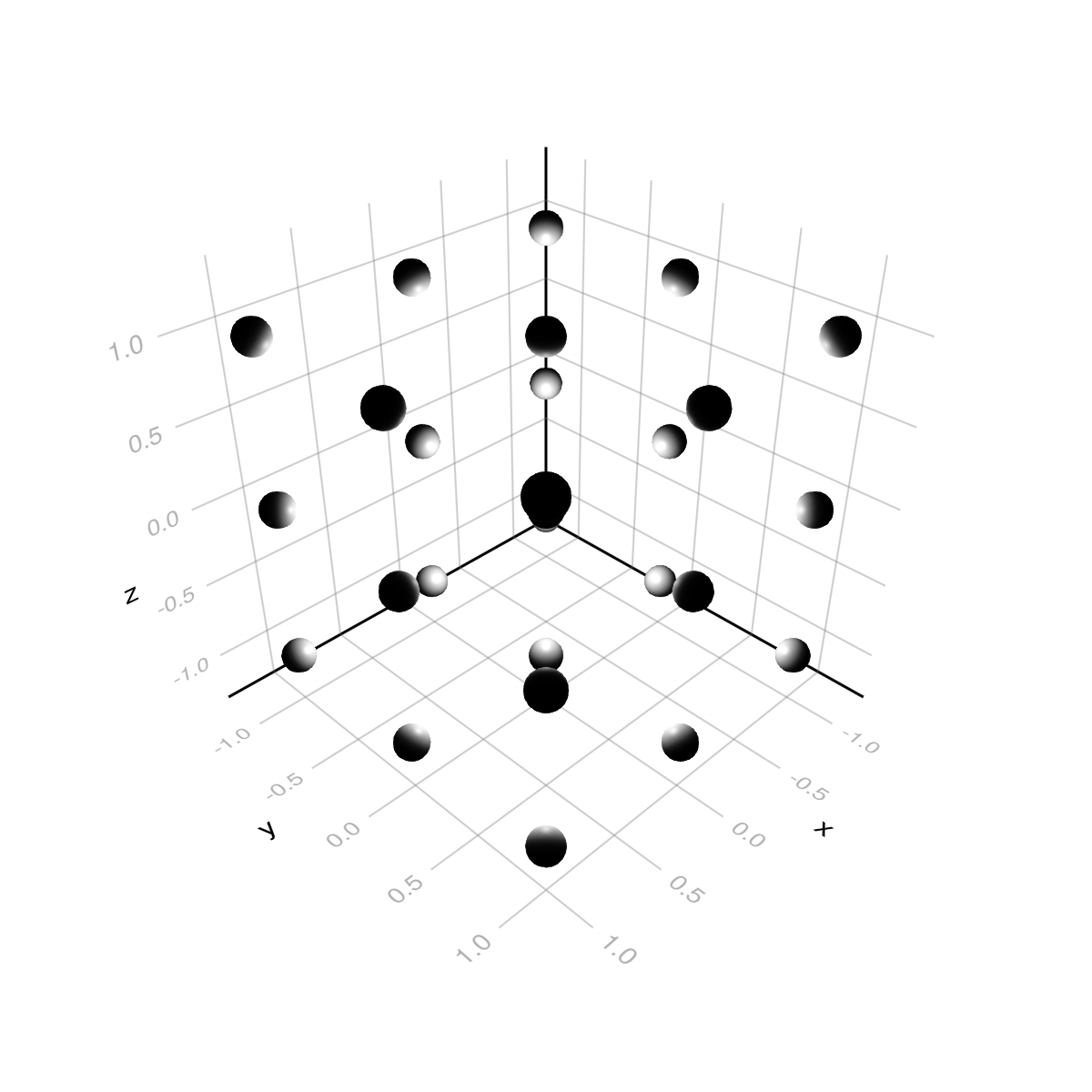
using GLMakie
lights = [
PointLight(RGBf(1, 1, 1), Point3f(0, 0, 5), 50),
PointLight(RGBf(2, 0, 0), Point3f(-3, -3, 2), 10),
PointLight(RGBf(0, 2, 0), Point3f(-3, 3, 2), 10),
PointLight(RGBf(0, 0, 2), Point3f( 3, 3, 2), 10),
PointLight(RGBf(2, 2, 0), Point3f( 3, -3, 2), 10),
]
fig = Figure(size = (600, 600))
ax = LScene(fig[1, 1], scenekw = (lights = lights,))
ps = [Point3f(x, y, 0) for x in -5:5 for y in -5:5]
meshscatter!(ax, ps, color = :white, markersize = 0.75)
scatter!(ax, map(l -> l.position[], lights), color = map(l -> l.color[], lights), strokewidth = 1, strokecolor = :black)
fig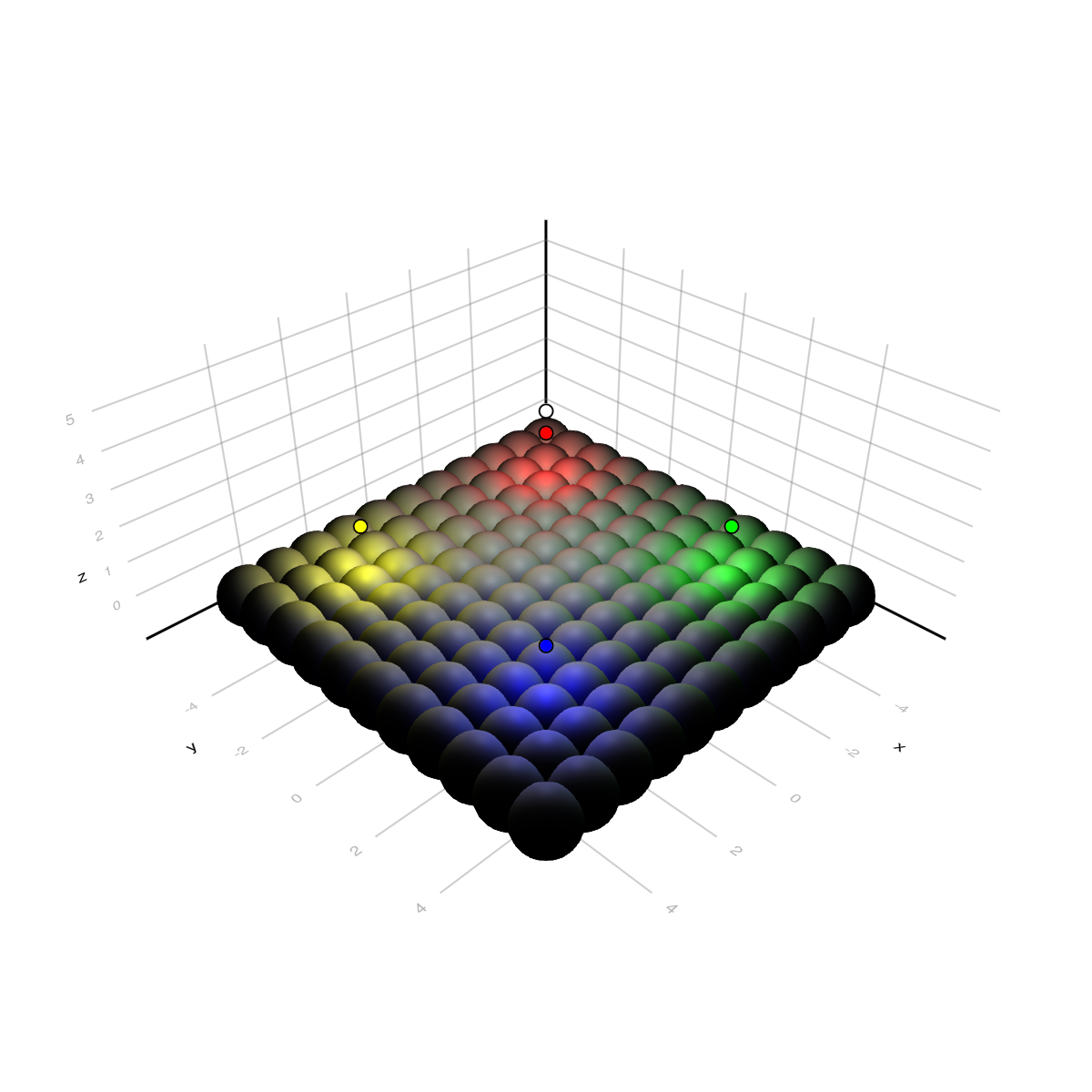
With a strong PointLight and Attenuation you can create different colors at different distances.
using GLMakie
using GeometryBasics
ps = [
Point3f(cosd(phi) * cosd(theta), sind(phi) * cosd(theta), sind(theta))
for theta in range(-20, 20, length = 21) for phi in range(60, 340, length=30)
]
faces = [QuadFace(30j + i, 30j + mod1(i+1, 30), 30*(j+1) + mod1(i+1, 30), 30*(j+1) + i) for j in 0:19 for i in 1:29]
marker_mesh = GeometryBasics.Mesh(meta(ps, normals = ps), decompose(GLTriangleFace, faces))
lights = [PointLight(RGBf(10, 4, 2), Point3f(0, 0, 0), 5)]
fig = Figure(size = (600, 600), backgroundcolor = :black)
ax = LScene(fig[1, 1], scenekw = (lights = lights,), show_axis = false)
update_cam!(ax.scene, ax.scene.camera_controls, Rect3f(Point3f(-2), Vec3f(4)))
meshscatter!(
ax, [Point3f(0) for _ in 1:14], marker = marker_mesh, markersize = 0.1:0.2:3.0,
color = :white, backlight = 1, transparency = false)
fig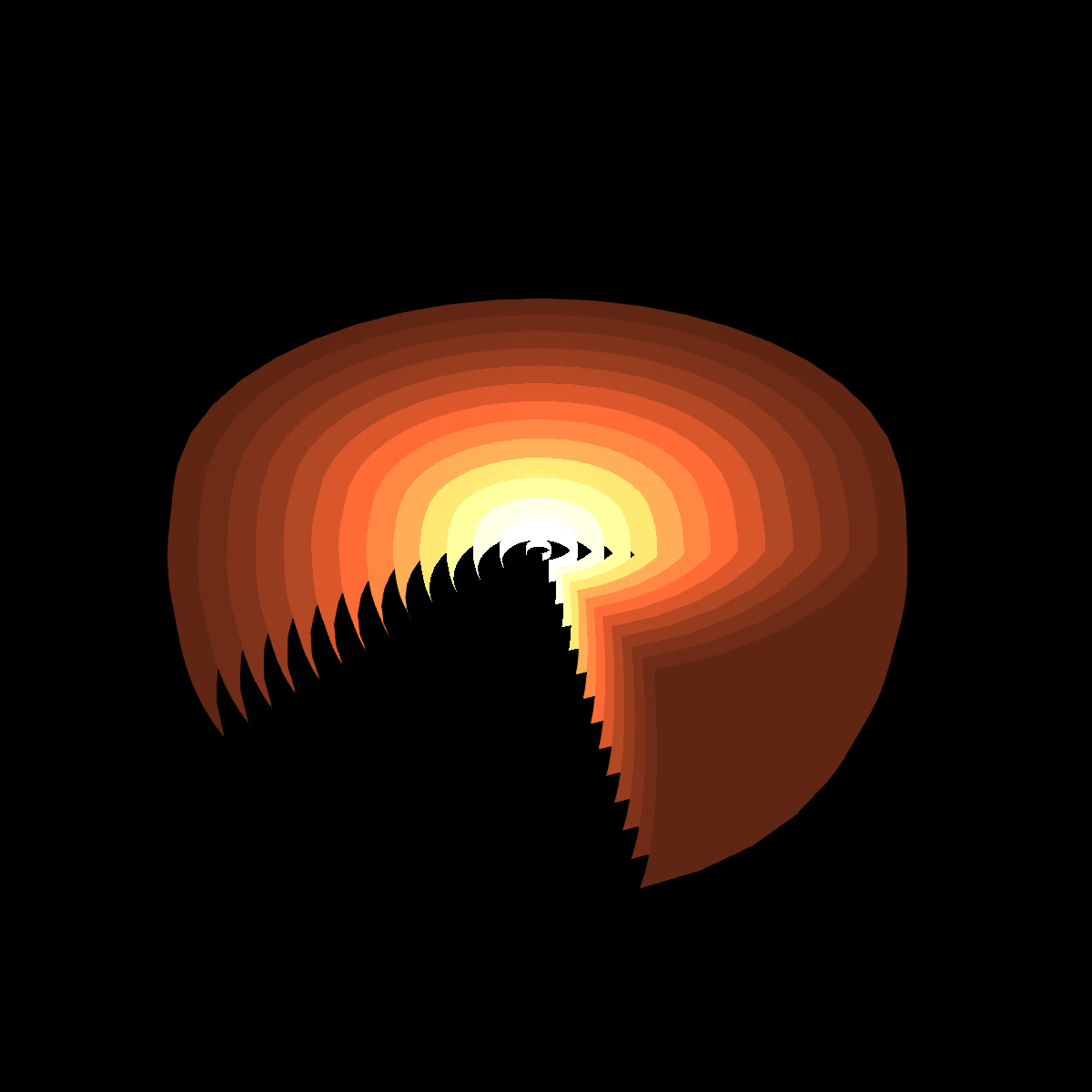
SpotLight
using GLMakie
lights = [
SpotLight(RGBf(1, 0, 0), Point3f(-3, 0, 3), Vec3f(0, 0, -1), Vec2f(0.0, 0.3pi)),
SpotLight(RGBf(0, 1, 0), Point3f( 0, 3, 3), Vec3f(0, -0.5, -1), Vec2f(0.2pi, 0.25pi)),
SpotLight(RGBf(0, 0, 1), Point3f( 3, 0, 3), Vec3f(0, 0, -1), Vec2f(0.25pi, 0.25pi)),
]
fig = Figure(size = (600, 600))
ax = LScene(fig[1, 1], scenekw = (lights = lights,))
ps = [Point3f(x, y, 0) for x in -5:5 for y in -5:5]
meshscatter!(ax, ps, color = :white, markersize = 0.75)
scatter!(ax, map(l -> l.position[], lights), color = map(l -> l.color[], lights), strokewidth = 1, strokecolor = :black)
fig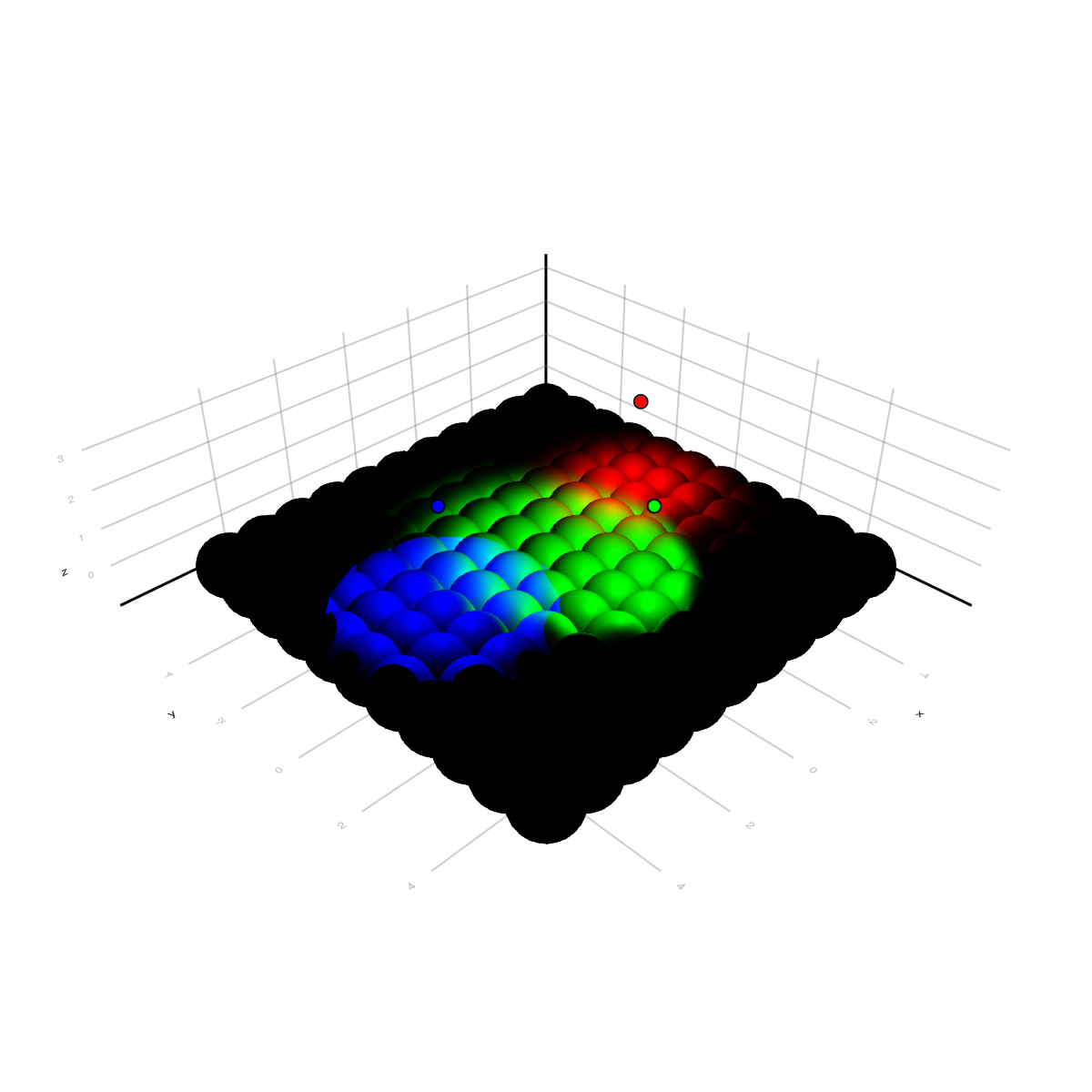
RectLight
using GLMakie
using FileIO, GeometryBasics, LinearAlgebra
# Create mesh from RectLight parameters
function to_mesh(l::RectLight)
n = -normalize(cross(l.u1[], l.u2[]))
p = l.position[] - 0.5 * l.u1[] - 0.5 * l.u2[]
positions = [p, p + l.u1[], p + l.u2[], p + l.u1[] + l.u2[]]
faces = GLTriangleFace[(1,2,3), (2,3,4)]
normals = [n,n,n,n]
return GeometryBasics.Mesh(meta(positions, normals = normals), faces)
end
fig = Figure(backgroundcolor = :black)
# Prepare lights
lights = Makie.AbstractLight[
AmbientLight(RGBf(0.1, 0.1, 0.1)),
RectLight(RGBf(0.9, 1, 0.8), Rect2f(-1.9, -1.9, 1.8, 1.8)),
RectLight(RGBf(0.9, 1, 0.8), Rect2f(-1.9, 0.1, 1.8, 1.8)),
RectLight(RGBf(0.9, 1, 0.8), Rect2f( 0.1, 0.1, 1.8, 1.8)),
RectLight(RGBf(0.9, 1, 0.8), Rect2f( 0.1, -1.9, 1.8, 1.8)),
]
for l in lights
if l isa RectLight
angle = pi/4
p = l.position[]
Makie.rotate!(l, Vec3f(0, 1, 0), angle)
p = 3 * Vec3f(1+sin(angle), 0, cos(angle)) +
p[1] * normalize(l.u1[]) +
p[2] * normalize(l.u2[])
translate!(l, p)
end
end
# Set scene
scene = LScene(
fig[1, 1], show_axis = false,
scenekw=(lights = lights, backgroundcolor = :black, center = false),
)
# floor
msh = mesh!(scene, Rect3f(Point3f(-10, -10, 0.01), Vec3f(20, 20, 0.02)), color = :white)
translate!(msh, 0, 0, -5)
# Cat
cat_mesh = FileIO.load(Makie.assetpath("cat.obj"))
cat_texture = FileIO.load(Makie.assetpath("diffusemap.png"))
p2 = mesh!(scene, cat_mesh, color = cat_texture)
Makie.rotate!(p2, Vec3f(1,0,0), pi/2)
translate!(p2, -2, 2, -5)
scale!(p2, Vec3f(4))
# Window/light source markers
for l in lights
if l isa RectLight
mesh!(to_mesh(l), color = :white, backlight = 1)
end
end
# place camera
update_cam!(scene.scene, Vec3f(1.5, -13, 2), Vec3f(1, -2, 0), Vec3f(0, 0, 1))
fig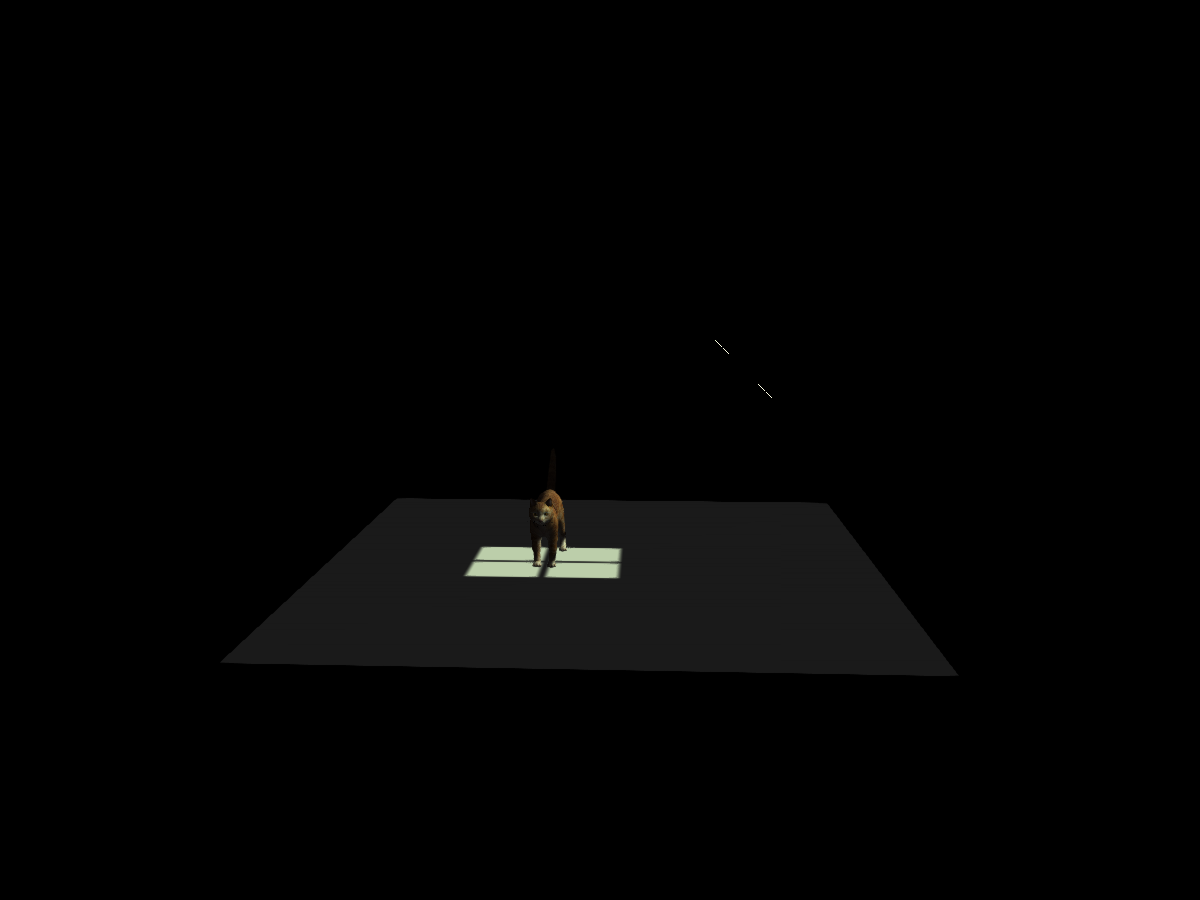
EnvironmentLight