scatter
scatter(positions)
scatter(x, y)
scatter(x, y, z)
Plots a marker for each element in
(x, y, z)
,
(x, y)
, or
positions
.
Attributes
Specific to
Scatter
-
cycle::Vector{Symbol} = [:color]sets which attributes to cycle when creating multiple plots. -
marker::Union{Symbol, Char, Matrix{<:Colorant}, BezierPath, Polygon}sets the scatter marker. -
markersize::Union{<:Real, Vec2f} = 9sets the size of the marker. -
markerspace::Symbol = :pixelsets the space in whichmarkersizeis given. SeeMakie.spaces()for possible inputs. -
strokewidth::Real = 0sets the width of the outline around a marker. -
strokecolor::Union{Symbol, <:Colorant} = :blacksets the color of the outline around a marker. -
glowwidth::Real = 0sets the size of a glow effect around the marker. -
glowcolor::Union{Symbol, <:Colorant} = (:black, 0)sets the color of the glow effect. -
rotations::Union{Real, Billboard, Quaternion} = Billboard(0f0)sets the rotation of the marker. ABillboardrotation is always around the depth axis. -
transform_marker::Bool = falsecontrols whether the model matrix (without translation) applies to the marker itself, rather than just the positions. (If this is true,scale!androtate!will affect the marker.)
Generic
-
visible::Bool = truesets whether the plot will be rendered or not. -
overdraw::Bool = falsesets whether the plot will draw over other plots. This specifically means ignoring depth checks in GL backends. -
transparency::Bool = falseadjusts how the plot deals with transparency. In GLMakietransparency = trueresults in using Order Independent Transparency. -
fxaa::Bool = falseadjusts whether the plot is rendered with fxaa (anti-aliasing). Note that scatter plots already include a different form of anti-aliasing when plotting non-image markers. -
inspectable::Bool = truesets whether this plot should be seen byDataInspector. -
depth_shift::Float32 = 0f0adjusts the depth value of a plot after all other transformations, i.e. in clip space, where0 <= depth <= 1. This only applies to GLMakie and WGLMakie and can be used to adjust render order (like a tunable overdraw). -
model::Makie.Mat4fsets a model matrix for the plot. This replaces adjustments made withtranslate!,rotate!andscale!. -
colorsets the color of the plot. It can be given as a named colorSymbolor aColors.Colorant. Transparency can be included either directly as an alpha value in theColorantor as an additional float in a tuple(color, alpha). The color can also be set for each scattered marker by passing aVectorof colors or be used to index thecolormapby passing aRealnumber orVector{<: Real}. -
colormap::Union{Symbol, Vector{<:Colorant}} = :viridissets the colormap that is sampled for numericcolors. -
colorrange::Tuple{<:Real, <:Real}sets the values representing the start and end points ofcolormap. -
nan_color::Union{Symbol, <:Colorant} = RGBAf(0,0,0,0)sets a replacement color forcolor = NaN. -
space::Symbol = :datasets the transformation space for positions of markers. SeeMakie.spaces()for possible inputs.
Examples
Using x and y vectors
Scatters can be constructed by passing a list of x and y coordinates.
using CairoMakie
xs = range(0, 10, length = 30)
ys = 0.5 .* sin.(xs)
scatter(xs, ys) Using points
It is also possible to pass coordinates as a vector of points, which is preferred if the coordinates should be updated later, to avoid different lengths of x and y.
Attributes like
color
and
markersize
can be set in scalar or vector form. If you pass a vector of numbers for
color
, the attribute
colorrange
which is by default automatically equal to the extrema of the color values, decides how colors are looked up in the
colormap
.
using CairoMakie
xs = range(0, 10, length = 30)
ys = 0.5 .* sin.(xs)
points = Point2f.(xs, ys)
scatter(points, color = 1:30, markersize = range(5, 30, length = 30),
colormap = :thermal) Markers
There are a couple different categories of markers you can use with
scatter
:
-
Chars like'x'or'α'. The glyphs are taken from Makie's default fontTeX Gyre Heros Makie. -
BezierPathobjects which can be used to create custom marker shapes. Most default markers which are accessed by symbol such as:circleor:rectconvert toBezierPaths internally. -
Polygons, which are equivalent to constructingBezierPaths exclusively out ofLineTocommands. -
Matrix{<:Colorant}objects which are plotted as image scatters. -
Special markers like
CircleandRectwhich have their own backend implementations and can be faster to display.
Default markers
Here is an example plot showing different shapes that are accessible by
Symbol
s, as well as a few characters.
using CairoMakie
markers_labels = [
(:circle, ":circle"),
(:rect, ":rect"),
(:diamond, ":diamond"),
(:hexagon, ":hexagon"),
(:cross, ":cross"),
(:xcross, ":xcross"),
(:utriangle, ":utriangle"),
(:dtriangle, ":dtriangle"),
(:ltriangle, ":ltriangle"),
(:rtriangle, ":rtriangle"),
(:pentagon, ":pentagon"),
(:star4, ":star4"),
(:star5, ":star5"),
(:star6, ":star6"),
(:star8, ":star8"),
(:vline, ":vline"),
(:hline, ":hline"),
('a', "'a'"),
('B', "'B'"),
('↑', "'\\uparrow'"),
('😄', "'\\:smile:'"),
('✈', "'\\:airplane:'"),
]
f = Figure()
ax = Axis(f[1, 1], yreversed = true,
xautolimitmargin = (0.15, 0.15),
yautolimitmargin = (0.15, 0.15)
)
hidedecorations!(ax)
for (i, (marker, label)) in enumerate(markers_labels)
p = Point2f(fldmod1(i, 6)...)
scatter!(p, marker = marker, markersize = 20, color = :black)
text!(p, text = label, color = :gray70, offset = (0, 20),
align = (:center, :bottom))
end
f Markersize
The
markersize
attribute scales the scatter size relative to the scatter marker's base size. Therefore,
markersize
cannot be directly understood in terms of a unit like
px
, it depends on
what
is scaled.
For
Char
markers,
markersize
is equivalent to the font size when displaying the same characters using
text
.
using CairoMakie
f, ax, sc = scatter(1, 1, marker = 'A', markersize = 50)
text!(2, 1, text = "A", textsize = 50, align = (:center, :center))
xlims!(ax, -1, 4)
f
The default
BezierPath
markers like
:circle
,
:rect
,
:utriangle
, etc. have been chosen such that they approximately match
Char
markers of the same markersize. This makes it easier to switch out markers without the overall look changing too much. However, both
Char
and
BezierPath
markers are not exactly
markersize
high or wide. We can visualize this by plotting some
Char
s,
BezierPath
s,
Circle
and
Rect
in front of a line of width
50
. You can see that only the special markers
Circle
and
Rect
match the line width because their base size is 1 x 1, however they don't match the
Char
s or
BezierPath
s very well.
using CairoMakie
f, ax, l = lines([0, 1], [1, 1], linewidth = 50, color = :gray80)
for (marker, x) in zip(['X', 'x', :circle, :rect, :utriangle, Circle, Rect], range(0.1, 0.9, length = 7))
scatter!(ax, x, 1, marker = marker, markersize = 50, color = :black)
end
f
If you need a marker that has some exact base size, so that you can match it with lines or other plot objects of known size, or because you want to use the marker in data space, you can construct it yourself using
BezierPath
or
Polygon
. A marker with a base size of 1 x 1, e.g., will be scaled like
lines
when
markersize
and
linewidth
are the same, just like
Circle
and
Rect
markers.
Here, we construct a hexagon polygon with radius
1
, which we can then use to tile a surface in data coordinates by setting
markerspace = :data
.
using CairoMakie
hexagon = Makie.Polygon([Point2f(cos(a), sin(a)) for a in range(1/6 * pi, 13/6 * pi, length = 7)])
points = Point2f[(0, 0), (sqrt(3), 0), (sqrt(3)/2, 1.5)]
scatter(points,
marker = hexagon,
markersize = 1,
markerspace = :data,
color = 1:3,
axis = (; aspect = 1, limits = (-2, 4, -2, 4))) Bezier path markers
Bezier paths are the basis for vector graphic formats such as svg and pdf and consist of a couple different operations that can define complex shapes.
A
BezierPath
contains a vector of path commands, these are
MoveTo
,
LineTo
,
CurveTo
,
EllipticalArc
and
ClosePath
. A filled shape should start with
MoveTo
and end with
ClosePath
.
Note
Unfilled markers (like a single line or curve) are possible in CairoMakie but not in GLMakie and WGLMakie, because these backends have to render the marker as a filled shape to a texture first. If no filling can be rendered, the marker will be invisible. CairoMakie, on the other hand can stroke such markers without problem.
Here is an example with a simple arrow that is centered on its tip, built from path elements.
using CairoMakie
arrow_path = BezierPath([
MoveTo(Point(0, 0)),
LineTo(Point(0.3, -0.3)),
LineTo(Point(0.15, -0.3)),
LineTo(Point(0.3, -1)),
LineTo(Point(0, -0.9)),
LineTo(Point(-0.3, -1)),
LineTo(Point(-0.15, -0.3)),
LineTo(Point(-0.3, -0.3)),
ClosePath()
])
scatter(1:5,
marker = arrow_path,
markersize = range(20, 50, length = 5),
rotations = range(0, 2pi, length = 6)[1:end-1],
) Holes
Paths can have holes, just start a new subpath with
MoveTo
that is inside the main path. The holes have to be in clockwise direction if the outside is in anti-clockwise direction, or vice versa. For example, a circle with a square cut out can be made by one
EllipticalArc
that goes anticlockwise, and a square inside which goes clockwise:
using CairoMakie
circle_with_hole = BezierPath([
MoveTo(Point(1, 0)),
EllipticalArc(Point(0, 0), 1, 1, 0, 0, 2pi),
MoveTo(Point(0.5, 0.5)),
LineTo(Point(0.5, -0.5)),
LineTo(Point(-0.5, -0.5)),
LineTo(Point(-0.5, 0.5)),
ClosePath(),
])
scatter(1:5,
marker = circle_with_hole,
markersize = 30,
) Construction from svg path strings
You can also create a bezier path from an
svg path specification string
. You can automatically resize the path and flip the y-axis (svgs usually have a coordinate system where y increases downwards) with the keywords
fit
and
yflip
. By default, the bounding box for the fitted path is a square of width 1 centered on zero. You can pass a different bounding
Rect
with the
bbox
keyword argument. By default, the aspect of the path is left intact, and if it's not matching the new bounding box, the path is centered so it fits inside. Set
keep_aspect = false
to squeeze the path into the bounding box, disregarding its original aspect ratio.
Here's an example with an svg string that contains the bat symbol:
using CairoMakie
batsymbol_string = "M96.84 141.998c-4.947-23.457-20.359-32.211-25.862-13.887-11.822-22.963-37.961-16.135-22.041 6.289-3.005-1.295-5.872-2.682-8.538-4.191-8.646-5.318-15.259-11.314-19.774-17.586-3.237-5.07-4.994-10.541-4.994-16.229 0-19.774 21.115-36.758 50.861-43.694.446-.078.909-.154 1.372-.231-22.657 30.039 9.386 50.985 15.258 24.645l2.528-24.367 5.086 6.52H103.205l5.07-6.52 2.543 24.367c5.842 26.278 37.746 5.502 15.414-24.429 29.777 6.951 50.891 23.936 50.891 43.709 0 15.136-12.406 28.651-31.609 37.267 14.842-21.822-10.867-28.266-22.549-5.549-5.502-18.325-21.147-9.341-26.125 13.886z"
batsymbol = BezierPath(batsymbol_string, fit = true, flipy = true)
scatter(1:10, marker = batsymbol, markersize = 50, color = :black) Polygon markers
One can also use
GeometryBasics.Polgyon
as a marker. A polygon always needs one vector of points which forms the outline. It can also take an optional vector of vectors of points, each of which forms a hole in the outlined shape.
In this example, a small circle is cut out of a larger circle:
using CairoMakie, GeometryBasics
p_big = decompose(Point2f, Circle(Point2f(0), 1))
p_small = decompose(Point2f, Circle(Point2f(0), 0.5))
scatter(1:4, fill(0, 4), marker=Polygon(p_big, [p_small]), markersize=100, color=1:4, axis=(limits=(0, 5, -1, 1),)) Marker rotation
Markers can be rotated using the
rotations
attribute, which also allows to pass a vector.
using CairoMakie
points = [Point2f(x, y) for y in 1:10 for x in 1:10]
rotations = range(0, 2pi, length = length(points))
scatter(points, rotations = rotations, markersize = 20, marker = '↑') Vec markersize
You can scale x and y dimension of markers separately by passing a
Vec
.
using CairoMakie
f = Figure()
ax = Axis(f[1, 1])
scales = range(0.5, 1.5, length = 10)
for (i, sx) in enumerate(scales)
for (j, sy) in enumerate(scales)
scatter!(ax, Point2f(i, j),
marker = '✈',
markersize = 30 .* Vec2f(sx, sy),
color = :black)
end
end
f Marker space
By default marker sizes are given in pixel units. You can change this by adjusting
markerspace
. For example, you can have a marker scaled in data units by setting
markerspace = :data
.
using CairoMakie
f = Figure()
ax = Axis(f[1, 1])
limits!(ax, -10, 10, -10, 10)
scatter!(ax, Point2f(0, 0), markersize = 20, markerspace = :data,
marker = '✈', label = "markerspace = :data")
scatter!(ax, Point2f(0, 0), markersize = 20, markerspace = :pixel,
marker = '✈', label = "markerspace = :pixel")
axislegend(ax)
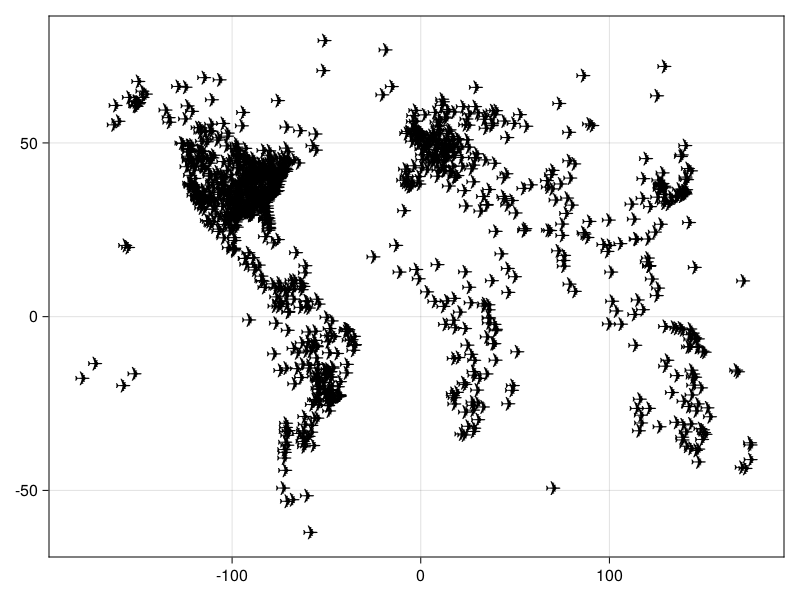
f Airport locations example
using CairoMakie
using DelimitedFiles
a = readdlm(assetpath("airportlocations.csv"))
scatter(a[1:50:end, :], marker = '✈',
markersize = 20, color = :black) These docs were autogenerated using Makie: v0.18.4, GLMakie: v0.7.4, CairoMakie: v0.9.4, WGLMakie: v0.7.4